AP BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE
INTRODUCTION
TO THE STUDY OF LIFE
1.
Chapter 1 presents unifying themes of
biology. Briefly describe each of these in your own words:
a. hierarchy of
organization g.
regulatory mechanisms
b. emergent
properties h.
unity and diversity
c. cellular
basis of life i. evolution
d. heritable
information j.
science as a process
e. correlation
of structure and function k.
science and technology
f. interaction
of organisms with their environment l.
biology is multidisciplinary
2.
Copy on your notebook paper and fill in
the chart below for the major subatomic particles of an atom.
|
Particle |
Charge |
Mass |
Location |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.
Atoms can have various numbers associated
with them.
a.
Define the following and show where each of
them is placed relative to the symbol of an element such C: atomic number, mass
number, and atomic weight.
b. Define
valance.
c.
Which of these four numbers is most
related to the chemical behavior of an atom? Explain.
4.
Explain what is meant by saying that the
sharing of electrons between atoms falls on a continuum from covalent bonds to
ionic bonds.
5.
Copy on your notebook paper and fill in
the table below that summarizes the properties of water that contribute to the
fitness of the environment for life.
|
Property |
Explanation of Property |
Example of Benefit to Life |
|
a. |
Hydrogen bonds hold molecules together
and adhere them to hydrophilic surfaces. |
b. |
|
High specific heat |
c. |
Temperature changes in environment and
organisms are moderated. |
|
d. |
Hydrogen bonds must be broken for water
to evaporate. |
e. |
|
f. |
Water molecules with high kinetic energy
evaporate; remaining molecules are cooler. |
g. |
|
Ice floats |
h. |
i. |
|
j. |
k. |
Most chemical reactions in life involve solutes
dissolved in water. |
6.
To become proficient in the use of the
concepts relating to pH, develop a concept map to organize your understanding
of the following terms: pH, [H+],
[OH-], acidic, basic, neutral, buffer, 1-14, acid-base pair. Remember
to label connecting lines and add additional concepts as you need them.
7.
Construct a concept map that illustrates
your understanding of the characteristics and significance of the three types
of isomers.
8.
Copy on your notebook paper and fill in
the following table on the functional groups.
|
Functional Group |
Molecular Formula |
Names and Characteristics of Organic Compounds Containing Functional Groups |
|
|
–OH |
|
|
|
|
Aldehyde or ketone; polar group |
|
Carboxyl |
|
|
|
|
–NH2 |
|
|
|
|
Thiols; cross-links stabilize protein
structure |
|
Phosphate |
|
|
9.
Describe the four structural levels in the
conformation of a protein.
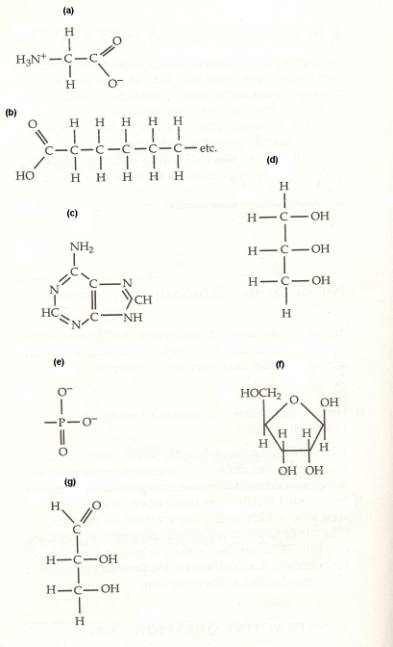
10. Identify
the type of monomer or group shown by these formulae. Then match the chemical formulae
with their description. Answers may be used more than once.
- Molecules that would combine to form a fat
- Molecule that would be attached to other monomers by a
peptide bond
- Molecules or groups that would combine to form a nucleotide
- Molecules that are carbohydrates
- Molecule that is a purine
- Monomer of a protein
- Groups that would be joined by phosodiester bonds